Delving into the realm of business appraisal excess inventory, this comprehensive guide unravels the intricate tapestry of excess inventory, its impact on businesses, and the strategies to navigate its complexities.
Excess inventory, a prevalent challenge faced by businesses, can lead to significant financial burdens and operational inefficiencies. This guide provides a roadmap to understanding the causes, consequences, and effective management of excess inventory, empowering businesses to optimize their operations and maximize profitability.
Business Appraisal Excess Inventory

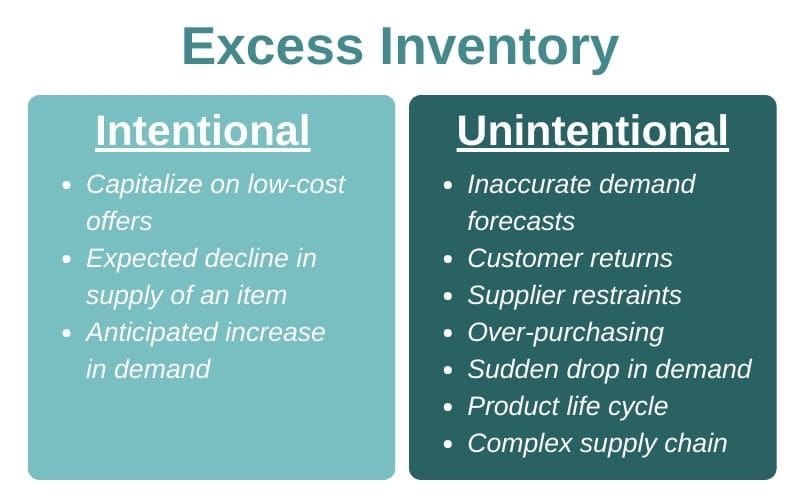
Excess inventory refers to the stock of goods that exceeds the amount a business can reasonably sell or use in the normal course of operations. Holding excess inventory can have a significant impact on businesses, affecting their financial performance, efficiency, and overall profitability.
Causes and Consequences of Excess Inventory
Excess inventory can result from various factors, including inaccurate demand forecasting, overproduction, poor inventory management practices, and disruptions in the supply chain. The consequences of holding excess inventory include increased storage costs, reduced profit margins, and potential obsolescence of products.
Identifying and Measuring Excess Inventory
Identifying and measuring excess inventory is crucial for businesses to optimize their inventory levels. Several methods can be used, such as the ABC analysis, which categorizes inventory items based on their value and usage, and the safety stock analysis, which determines the minimum inventory level required to meet demand without stockouts.
Valuation of Excess Inventory
Excess inventory refers to the stock of goods that exceeds the demand or forecasted sales. Valuing excess inventory is crucial for businesses to determine its impact on financial statements and make informed decisions regarding its disposal. Several methods are available for valuing excess inventory, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Methods for Valuing Excess Inventory
- Cost Method:Values excess inventory at its acquisition cost, including purchase price, freight, and handling charges. This method is straightforward and provides a conservative estimate of value.
- Market Value Method:Values excess inventory at its current market price, which may be lower than the cost due to factors such as obsolescence or oversupply. This method provides a more realistic estimate of value but can be difficult to determine accurately.
- Net Realizable Value Method:Values excess inventory at the estimated selling price minus the estimated costs of completion, disposal, and profit margin. This method provides a more optimistic estimate of value but requires detailed analysis of potential sales and costs.
Factors to Consider When Valuing Excess Inventory
When valuing excess inventory, several factors should be considered:
- Age and Condition:Older or damaged inventory may have a lower value than newer, undamaged inventory.
- Obsolescence:Inventory that is outdated or no longer in demand may have little or no value.
- Market Conditions:Excess inventory may be more difficult to sell in a slow market, which can affect its value.
- Storage Costs:The cost of storing excess inventory can impact its value, especially over time.
Examples of Calculating the Value of Excess Inventory
Using the cost method, if an item was purchased for $10 and has not depreciated, its value would be $10. Using the market value method, if the same item can be sold for $7 due to market conditions, its value would be $7.
Using the net realizable value method, if the item can be sold for $12 after deducting $3 for completion costs and a $2 profit margin, its value would be $9.
Disposal of Excess Inventory
Excess inventory can be a significant financial burden for businesses. To mitigate this issue, it’s crucial to implement effective disposal strategies. Various methods exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
Sales and Promotions
Selling excess inventory through discounts, promotions, and clearance sales can generate revenue and reduce storage costs. However, it may result in lower profit margins and potential damage to brand reputation if products are sold at deep discounts.
Liquidation
Liquidation involves selling excess inventory in bulk to a liquidator at a reduced price. This method allows businesses to quickly dispose of large quantities of inventory but typically results in significant losses.
Donation, Business appraisal excess inventory
Donating excess inventory to charitable organizations can provide tax benefits and enhance corporate social responsibility. However, it may not be suitable for all types of inventory or if there are restrictions on donations.
Return to Supplier
Returning excess inventory to the supplier is an option if the supplier’s return policy allows it. This method eliminates storage costs and potential losses, but it may not always be possible or cost-effective.
Scrap or Disposal
In cases where other disposal methods are not viable, businesses may consider scrapping or disposing of excess inventory. This involves physically destroying or discarding the products, which may incur disposal costs and potential environmental concerns.
Financial Impact of Excess Inventory: Business Appraisal Excess Inventory
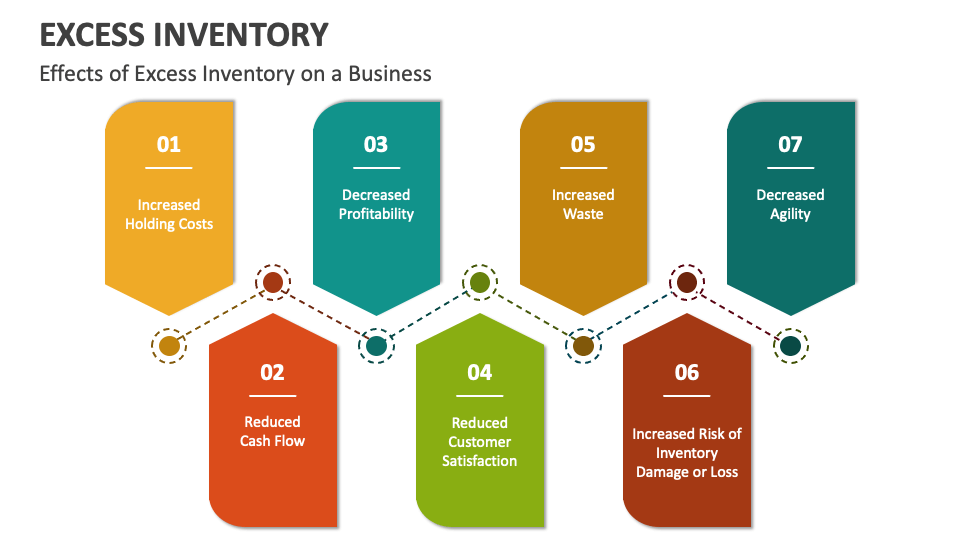
Excess inventory can have a significant impact on a company’s financial statements. It can tie up cash, reduce profitability, and increase the risk of obsolescence. The carrying cost of excess inventory can also be a significant expense.
The impact of excess inventory on financial statements can be seen in the following ways:
- Reduced profitability:Excess inventory can reduce profitability by tying up cash that could be used for other purposes, such as investing in new products or expanding operations.
- Increased risk of obsolescence:Excess inventory is more likely to become obsolete, which can result in a loss of value.
- Increased carrying costs:Excess inventory incurs carrying costs, such as storage, insurance, and handling. These costs can add up over time and reduce profitability.
Tax Implications
Holding excess inventory can also have tax implications. In some cases, companies may be able to deduct the cost of excess inventory from their taxable income. However, this deduction is limited to the amount of inventory that is considered to be “normal” for the company’s business.
Any excess inventory beyond this amount may not be deductible.
In addition, companies may be required to pay taxes on the sale of excess inventory. The amount of tax that is owed will depend on the company’s tax rate and the value of the inventory.
Examples
Here are some examples of how excess inventory can affect financial performance:
- A company that manufactures clothing may have excess inventory if it produces too many items that do not sell. This can result in reduced profitability, as the company will have to sell the items at a discount or may even have to scrap them.
- A company that sells electronics may have excess inventory if it purchases too many items that become obsolete quickly. This can result in a loss of value, as the company will have to sell the items at a loss or may even have to scrap them.
- A company that operates a warehouse may have excess inventory if it stores too many items that are not needed. This can result in increased carrying costs, as the company will have to pay for the storage, insurance, and handling of the items.
Management of Excess Inventory
Excess inventory refers to the accumulation of unsold or obsolete stock that exceeds the actual demand. It can result from various factors such as inaccurate demand forecasting, overproduction, or changes in market trends. Managing excess inventory effectively is crucial for businesses to minimize financial losses and optimize inventory levels.
There are several strategies that businesses can adopt to manage excess inventory effectively:
- Sell-through efforts:Implement strategies such as discounts, promotions, and bundled deals to encourage customers to purchase excess inventory.
- Liquidation:Partner with liquidators or online marketplaces to sell excess inventory at a discounted price, minimizing losses.
- Repurposing or rebranding:Explore opportunities to repurpose or rebrand excess inventory to create new products or target different customer segments.
- Donation:Consider donating excess inventory to charitable organizations, which can help reduce storage costs and generate tax benefits.
- Scrap or disposal:As a last resort, businesses may need to scrap or dispose of excess inventory that has no value or cannot be sold.
Inventory management systems play a vital role in reducing excess inventory by providing real-time visibility into inventory levels, tracking demand patterns, and optimizing inventory replenishment. By leveraging data and analytics, businesses can make informed decisions about production, procurement, and inventory levels to minimize the risk of excess inventory.
Best practices for managing excess inventory include:
- Accurate demand forecasting:Use data and analytics to forecast demand accurately, considering factors such as seasonality, market trends, and customer behavior.
- Optimized inventory levels:Maintain optimal inventory levels based on demand patterns and lead times to avoid overstocking.
- Regular inventory audits:Conduct regular inventory audits to identify and track excess inventory, enabling timely decision-making.
- Effective inventory management systems:Implement robust inventory management systems to monitor inventory levels, track stock movements, and generate reports for analysis.
- Collaboration and communication:Foster collaboration between different departments, including sales, marketing, and operations, to align inventory management strategies and avoid excess inventory buildup.
By adopting these strategies and best practices, businesses can effectively manage excess inventory, minimize financial losses, and optimize inventory levels to support overall business performance.
Final Summary

In conclusion, business appraisal excess inventory presents a multifaceted challenge that requires careful consideration and proactive management. By understanding the methods for identifying, valuing, and disposing of excess inventory, businesses can mitigate its negative impact and harness its potential for financial optimization.
Embracing best practices in inventory management, leveraging technology, and implementing effective strategies will empower businesses to unlock the full potential of their inventory and drive sustainable growth.
Expert Answers
What are the key causes of excess inventory?
Inaccurate demand forecasting, overproduction, obsolete products, and inefficient inventory management practices are common causes of excess inventory.
How can businesses identify excess inventory?
Regular inventory audits, analysis of inventory turnover ratios, and monitoring of stock levels can help businesses identify excess inventory.
What are the financial implications of holding excess inventory?
Excess inventory can lead to increased storage costs, insurance expenses, and potential losses due to obsolescence or damage.